Difference between revisions of "Range Search"
m (spelling and grammar corrections, I was unsure what you meant in some places. I did my best to change these, but you should make sure I didn't remove anything you wanted to keep.) |
m (more corrections) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== Advantages == | == Advantages == | ||
| − | The main advantage of range search over the k-NN algorithm is that range search gets only corresponding data. The k-NN algorithm can | + | The main advantage of range search over the k-NN algorithm is that range search gets only corresponding data. The k-NN algorithm can get data points that do not correspond to the current situation if ''k'' is too high for the current data, or it may ignore relevant data, if ''k'' is much less than the number of data points 'around' the current situation |
== Illustrations == | == Illustrations == | ||
Revision as of 19:13, 8 August 2011
Range search is a data analysis algorithm, which is very similar to k-NN. The main difference is that k-NN gets a fixed number of data points while range search does not.
How it works
Record state (aka situation, turn snapshot, etc.) with some set of attributes (velocity, acceleration, x, y, etc.). When you need data, calculate some hypercube centered at the current situation. For example, if the current situation is {velocity = 8, acceleration = 0, x = 200, y = 200}, then hypercube can be described as the set of intervals {[6,8], [0,0], [180, 220], [180, 220]}. Then iterate through all data and select the points that are contained by this hypercube. Then use these data points for targeting, movement, etc.
Advantages
The main advantage of range search over the k-NN algorithm is that range search gets only corresponding data. The k-NN algorithm can get data points that do not correspond to the current situation if k is too high for the current data, or it may ignore relevant data, if k is much less than the number of data points 'around' the current situation
Illustrations
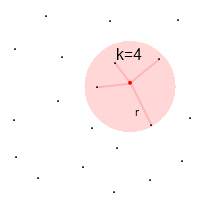
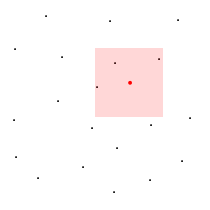
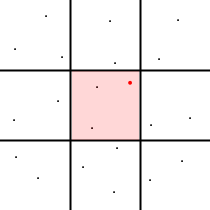
Legend:
- little black dots - data points
- big red dots - current situation
- red areas - area of data points used for data analysis
 |
 |
|
| k-nearest neighbours algorithm | Range search algorithm | Visit Count Stats algorithm |
See also
- Dynamic Clustering (k-nearest neighbors)
- Visit Count Stats